Water is the lifeblood of any homestead, but for urban growers, every drop counts. As cities expand and climate change intensifies, water scarcity is becoming a pressing issue. Many metropolitan areas now face stricter water restrictions, rising utility costs, and dwindling groundwater supplies. In places like Cape Town, which nearly reached “Day Zero” in 2018, and drought-stricken regions of the American Southwest, residents have had to rethink how they use water. Urban homesteaders—growing food, raising small livestock, and practicing sustainability in limited spaces—must be especially mindful of their water footprint.
Take the example of Maria, an urban homesteader in Austin, Texas. When her city imposed water restrictions during a severe drought, she transformed her backyard into a water-efficient oasis. By installing rain barrels, switching to drip irrigation, and mulching heavily, she cut her outdoor water use by 60%—without sacrificing her vegetable yields. Her story proves that with smart strategies, urban homesteaders can thrive even in water-scarce environments.
Cities are also stepping up to promote conservation. Many now offer rebates for rainwater harvesting systems, free smart irrigation controllers, and discounts on low-flow fixtures. Some, like Los Angeles and Melbourne, have implemented greywater recycling programs, allowing residents to reuse lightly used household water for irrigation. Urban homesteaders who take advantage of these programs not only save money but also contribute to broader sustainability efforts.
In this guide, we’ll explore practical, cost-effective ways to manage water wisely on an urban homestead. Whether you’re growing herbs on a balcony or keeping chickens in a tiny backyard, these tips will help you conserve water, reduce bills, and build a resilient, eco-friendly lifestyle. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Your Water Usage: A Guide for Urban Homesteaders
Water is a precious resource, especially in urban environments where supply may be limited or expensive. The first step to smarter water management is understanding how you use it. By tracking your consumption, identifying waste, and making data-driven adjustments, you can significantly reduce your water footprint—and your bills.
How Much Water Do You Really Use?
Not all water use is equal. Some activities consume far more than others. Here’s a breakdown of average water usage for common household tasks:

Key Takeaway: Outdoor irrigation and long showers are often the biggest water guzzlers. If you’re growing food, gardening alone can account for 50%+ of your summer water use—making efficiency critical.
How to Read Your Water Meter (And Detect Leaks)
Your water meter is a free, real-time tool to track usage. Here’s how to use it:
- Locate Your Meter – Usually near the street in a covered box labeled “Water.”
- Read the Numbers – Most meters display usage in gallons or cubic feet (1 cubic foot = 7.48 gallons).
- Check for Leaks – Turn off all water sources, then watch the meter:
- If the dial moves, you have a leak.
- A spinning leak indicator (small triangle or gear) confirms it.
- Track Daily Use – Record numbers at the same time each day to spot spikes.
Pro Tip: Some smart meters (like Flume) sync with apps to alert you to leaks automatically.
Best Apps for Tracking Water Consumption
Want to monitor usage without manual checks? These apps help:
📱 Flume Smart Home Water Monitor – Syncs with your meter for real-time tracking and leak alerts.
📱 WaterMinder – Logs daily water use and reminds you to hydrate (or conserve).
📱 Dropcountr – Connects to utility providers for personalized usage reports.
📱 Ecoisme – Tracks water and energy use, identifying waste hotspots.
Bonus: Some cities (like Los Angeles and Melbourne) offer free water-use dashboards through their utility websites.
Next Steps: Audit & Optimize
Now that you know where your water goes:
✅ Compare your usage to local averages (ask your utility for benchmarks).
✅ Fix leaks immediately—a dripping faucet wastes 3,000+ gallons/year.
✅ Set a monthly goal (e.g., “Reduce garden water by 20%”).
Up next: Rainwater harvesting—how to collect FREE water for your homestead.

Collecting and Storing Rainwater: A Smart Solution for Urban Homesteaders
Rainwater harvesting is one of the easiest ways to reduce your water bill, conserve resources, and keep your garden thriving—even during droughts. With the right setup, you can collect hundreds of gallons of free water each year. Here’s how to get started.
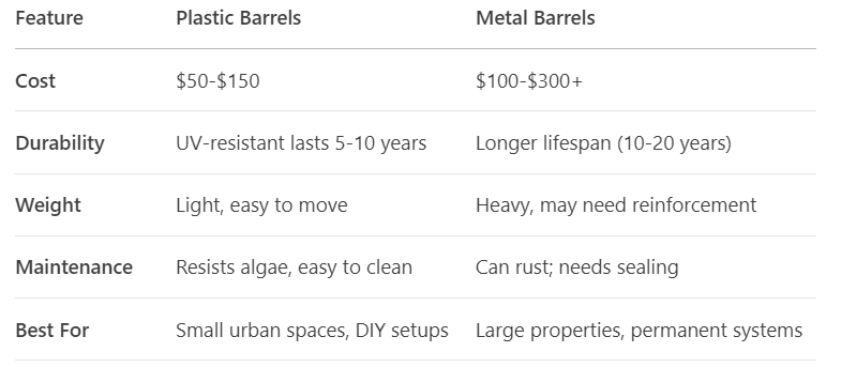
Choosing the Right Rain Barrel: Size & Material
Not all rain barrels are created equal. The best choice depends on your space, budget, and water needs.
Pro Tip:
- 50-80 gallons is ideal for most urban homesteads (fits under a downspout).
- Food-grade plastic (HDPE) is safest for edible gardens.
- Dark-colored barrels prevent algae growth.
Step-by-Step Rain Barrel Installation
What You’ll Need:
✔ Rain barrel with spigot & overflow valve
✔ Downspout diverter or flexible elbow
✔ Leveling base (cinder blocks or pavers)
✔ Drill & mesh screen (to keep out debris)
Installation Steps:
- Choose a Location – Near a downspout, on a stable, elevated base (helps with water pressure).
- Modify the Downspout – Cut it at barrel height and attach a diverter (or use a flexible elbow).
- Secure the Barrel – Place on a level surface to prevent tipping.
- Add a Filter – Cover the inlet with mesh to block leaves and mosquitoes.
- Connect Overflow – Run a hose from the overflow valve away from your foundation.
- Test the System – Wait for rain or simulate with a hose.
Safety Note: Always anchor barrels in windy areas—a full 55-gallon barrel weighs over 400 lbs!
Legal Considerations: Is Rainwater Harvesting Restricted?
While rainwater collection is legal in most places, some areas have restrictions:
✅ Encouraged (Rebates Available!) – States like Arizona, Texas, and Oregon offer tax incentives or discounts on barrels.
⚠ Regulated – Colorado (until 2016) and Utah require permits for large systems.
❌ Restricted – A few HOA communities ban visible rain barrels for aesthetic reasons.
How to Check Your Local Laws:
- Search “[Your State] + Rainwater Harvesting Laws”
- Call your local extension office or water utility
Pro Tip: Even in regulated areas, small-scale collection (under 100 gal) is usually allowed.
Maximizing Your Rainwater System
- Link multiple barrels with connectors for extra storage.
- Use a first-flush diverter to discard the dirtiest initial runoff.
- Winterize by draining barrels in freezing climates.
Up Next: Drip Irrigation—How to Water Your Garden with 90% Less Waste.
Efficient Irrigation Techniques for Urban Homesteaders
Watering your garden shouldn’t mean watching half of it evaporate or run off into the sidewalk. With the right irrigation system, you can cut water waste by up to 90% while keeping plants healthier. Let’s compare methods, build a budget-friendly DIY system, and explore smart tech for hassle-free watering.
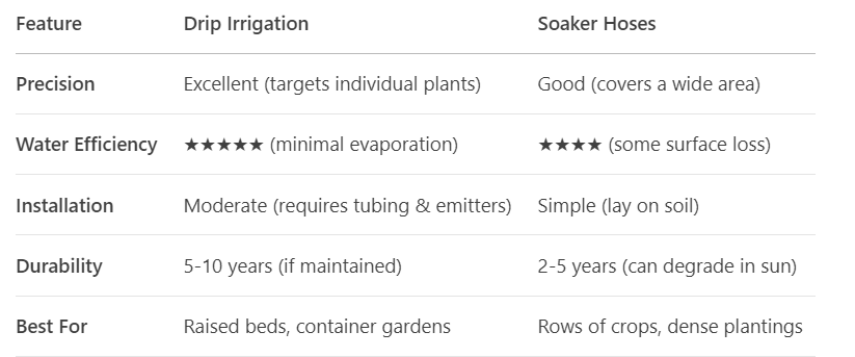
Drip Irrigation vs. Soaker Hoses: Which Is Best for You?
Both systems deliver water directly to plant roots, but they suit different needs:
Key Takeaways:
- Drip irrigation wins for customization—ideal for mixed gardens (e.g., tomatoes + herbs).
- Soaker hoses are cheaper and faster to install for large, uniform plots (like squash or beans).
How to Build a DIY Drip Irrigation System ($50 or Less!)
Materials Needed:
✔ ½” polyethylene tubing (main line)
✔ ¼” micro-tubing + drip emitters (adjustable flow)
✔ Pressure regulator (for tap hookups)
✔ Timer (optional but recommended)
✔ Hole punch & goof plugs (for mistakes!)
Step-by-Step Setup:
- Map Your Garden – Sketch where plants are and how much water they need (e.g., tomatoes > basil).
- Lay Main Tubing – Run ½” tubing along beds, securing with landscape stakes.
- Add Emitters – Punch holes, attach ¼” tubing, and place emitters at each plant’s base.
- Connect to Water – Attach a pressure regulator to your faucet/hose (prevents bursts).
- Test & Adjust – Run the system, checking for leaks and adjusting emitter flow rates.
Pro Tip: Use a $15 mechanical timer to automate watering at dawn (reduces evaporation).
Smart Irrigation Systems: Are They Worth It?
For tech-savvy homesteaders, these systems adjust watering based on weather, soil moisture, and plant needs:
Top Smart Irrigation Controllers
- Rachio 3 ($200-$300)
- Pros: Weather-aware, integrates with Alexa, saves 30-50% water.
- Cons: Requires strong Wi-Fi.
- Orbit B-hyve ($100-$180)
- Pros: Budget-friendly, no subscription, good for drip systems.
- Cons: App can be glitchy.
- RainMachine Touch HD-12 ($250)
- Pros: Works offline, hyper-local weather data.
- Cons: Pricier, bulky design.
Bonus: Soil Sensors
- $50-$150 devices (like Parrot Pot or Edyn) monitor soil moisture and alert you when plants are thirsty.
Final Tips for Efficient Watering
- Water early morning (before 10 AM) to reduce evaporation.
- Group plants by water needs (hydrozoning) to avoid over/under-watering.
- Mulch heavily (3-4″) to keep soil moist longer.
Next Up: Soil Secrets—How to Boost Water Retention Naturally.
Soil and Mulching Strategies to Slash Water Use
A thriving urban garden starts with healthy soil and smart mulching. The right ground cover can cut watering needs by 50% or more, suppress weeds, and even boost yields. Here’s how to choose the best mulch, test your soil’s water-holding power, and a real-world example of mulch magic in action.
Mulch Showdown: Straw vs. Wood Chips vs. Leaves
Not all mulches are created equal. Compare these popular options:
| Type | Best For | Pros | Cons |
| Straw | Veggie beds, annuals | Lightweight, decomposes fast (adds nutrients) | Can contain weed seeds |
| Wood Chips | Trees, perennials | Long-lasting, great for pathways | Ties up nitrogen early on |
| Leaves | Shady areas, compost | Free! Improves soil structure | Can mat down if not shredded |
Pro Tips:
- Straw: Layer 3-4″ thick to block weeds. Avoid hay (it’s a weed bomb).
- Wood chips: Use aged chips or add nitrogen fertilizer to balance decomposition.
- Leaves: Shred with a mower first—whole leaves smother plants.
How to Test Your Soil’s Moisture Retention
Wondering if your soil holds water like a sponge or a sieve? Try these DIY tests:
1. The Squeeze Test
- Grab a handful of damp soil.
- If it holds shape but crumbles when poked: Ideal (loamy soil).
- If it won’t hold shape: Too sandy (drains too fast).
- If it stays in a tight ball: Too clayy (holds too much water).
2. The Jar Test
- Fill a jar ⅓ with soil, ⅔ with water. Shake hard.
- Let settle for 24 hours.
- Sand sinks first (bottom layer).
- Silt (middle layer).
- Clay (top layer).
- Organic matter floats.
Fix Poor Retention:
- Sandy soil: Mix in compost or coconut coir.
- Clay soil: Add coarse sand + compost.
Case Study: The Mulch Miracle in Portland
The Problem:
Urban gardener Sarah K. struggled with daily watering in her 200 sq ft raised beds. Her sandy soil drained too fast, and summer temps wilted her greens.
The Solution:
She applied:
- 2″ of compost (to boost organic matter)
- 3″ of straw mulch (to slow evaporation)
The Results:
✅ Watering frequency dropped from daily to twice weekly.
✅ Tomato yields increased 30% (more consistent moisture).
✅ Weeding time cut in half.
Her Key Insight:
“Mulch acts like a slow-release water battery. Now I only water when I stick a finger under the mulch and feel dryness.”
Next Steps
- This weekend: Test your soil and mulch one bed.
- Next level: Try living mulch (clover, creeping thyme) between plants.
Coming Up: Greywater Recycling—Turn Shower Water into Garden Gold.
Greywater Recycling: Safe Ways to Reuse Household Water
Greywater—lightly used water from sinks, showers, and laundry—can be a game-changer for urban homesteaders, cutting outdoor water use by up to 40%. But doing it wrong can harm plants or even your health. Here’s how to recycle greywater safely and simply.
Greywater Safety 101: Avoiding Contaminants
Not all greywater is equal. Follow these rules to keep your garden (and yourself) safe:
🚫 Never Use:
- Water from washing diapers, pet waste, or raw meat (pathogen risk).
- Boron-heavy products (common in some detergents)—toxic to plants.
- Chlorine bleach or harsh chemicals (kills soil microbes).
✅ Safe Sources:
- Shower/bath water (mild soaps only).
- Bathroom sink water (toothpaste residue is fine).
- Laundry water (use plant-friendly detergents like ECOS or Oasis).
Key Precautions:
- No pooling—greywater should soak into soil within 30 minutes to avoid mosquitoes.
- Rotate application areas to prevent salt buildup.
- Wear gloves when handling greywater systems.
DIY Greywater Filter (Under $30!)
Turn a 5-gallon bucket into a basic filter for laundry-to-landscape systems:
Materials:
✔ 5-gallon bucket with lid
✔ 1’ of ½” PVC pipe
✔ Drill + ⅛” bit
✔ Gravel, sand, and activated charcoal (aquarium grade)
Steps:
- Drill holes in the bucket’s bottom and lid.
- Layer filtration media:
- Bottom: 1” gravel
- Middle: 2” sand
- Top: 1” charcoal
- Run PVC pipe from your washing machine’s drain hose into the bucket.
- Place bucket near garden beds—let filtered water drain via the holes.
Note: This is a basic pre-filter—ideal for non-edible plants. For veggies, consider a branched drain system (directs water underground).
Plants to NEVER Water with Greywater
Some plants are sensitive to salts, soaps, or pH shifts. Avoid using greywater on:
🌱 Leafy greens (lettuce, spinach)—absorb contaminants easily.
🍓 Berries (strawberries, raspberries)—prone to soap residue.
🍋 Citrus trees—hate salt buildup.
🌿 Herbs (basil, mint)—flavors can be affected.
Greywater-Friendly Plants:
✅ Fruit trees (apple, pear)
✅ Bamboo or ornamental grasses
✅ Native shrubs (lavender, rosemary)
Pro Tip:
Use greywater within 24 hours—storing it breeds bacteria.
Next Up: Drought-Resistant Plants—Keep Your Garden Thriving on Minimal Water.

Drought-Resistant Plants for Urban Homesteaders
Water scarcity doesn’t mean you have to give up a lush, productive garden. By choosing the right plants and redesigning your landscape, you can create a thriving oasis that sips water instead of guzzling it. Here are the best drought-tolerant edibles, pollinator-friendly flowers, and steps to transform a thirsty lawn into a water-wise paradise.
Top 10 Drought-Tolerant Vegetables & Herbs
These resilient plants produce abundant harvests with minimal watering once established:
Vegetables
- Okra – Thrives in heat, deep roots access subsoil moisture.
- Sweet Potatoes – Spreads vigorously, stores water in tubers.
- Pole Beans – More drought-hardy than bush varieties.
- Swiss Chard – Bounces back after dry spells.
- Peppers (Hot & Sweet) – Prefers infrequent, deep watering.
Herbs
- Rosemary – Mediterranean native, thrives on neglect.
- Thyme – Groundcover that resists scorching sun.
- Oregano – Spreads like a weed, fragrant and hardy.
- Lavender – Loves dry, sandy soil.
- Sage – Fuzzy leaves reduce water loss.
Pro Tip: Use olla pots (clay irrigation vessels) near roots to reduce watering needs by 50-70%.
Best Native Flowers for Pollinators (That Need Little Water)
Attract bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds with these low-water natives:
For Full Sun:
- Purple Coneflower (Echinacea) – Drought-tolerant, blooms for months.
- Black-Eyed Susan (Rudbeckia) – Self-seeds, thrives in poor soil.
- Blanket Flower (Gaillardia) – Fiery red/yellow blooms, zero fuss.
For Shade/Dry Areas:
- California Poppy (Eschscholzia) – Golden blooms, reseeds yearly.
- Yarrow (Achillea) – Feathery leaves, pink/white/yellow flowers.
Bonus: These plants often have deep taproots that break up compacted soil, improving water absorption.
How to Transition a Lawn to a Drought-Resistant Landscape
Replacing grass with water-wise plants cuts outdoor water use by 60-90%. Here’s how to do it:
Step 1: Kill the Grass (Without Chemicals)
- Sheet Mulching: Smother grass with cardboard + 6” of wood chips (takes 3-6 months).
- Solarization: Cover lawn with clear plastic in summer (4-6 weeks).
Step 2: Choose Your New Landscape Style
- Xeriscape: Gravel paths + succulents (agave, sedum).
- Food Forest: Fruit trees + edible groundcovers (purslane, nasturtium).
- Meadowscape: Native grasses + wildflowers.
Step 3: Plant Strategically
- Group plants by water needs (hydrozoning).
- Use swales (shallow trenches) to capture rainwater.
- Mulch deeply (3-4”) to retain moisture.
Case Study: A Seattle family replaced their 1,000 sq ft lawn with drought-resistant clover and native strawberries. Result? No watering needed after establishment, and they gained a pollinator haven.
Final Tip: Train Plants to Be Thirstier
- Water deeply but infrequently to encourage deep roots.
- Let plants wilt slightly between waterings to build resilience.
Next Up: Fixing Leaks—How to Stop Wasting Hundreds of Gallons Yearly.
Fixing Leaks and Optimizing Plumbing: Stop Wasting Water & Money
Even small leaks can waste thousands of gallons a year—draining your wallet and precious resources. Here’s how to hunt down hidden leaks, upgrade to water-saving fixtures, and use smart tech to protect your homestead from costly water damage.
How to Perform a Home Leak Audit (30 Minutes or Less!)
Step 1: Check Your Water Meter
- Turn off all water sources (no faucets, appliances, or irrigation).
- Note the meter reading, wait 1 hour, then check again.
- If the numbers changed, you have a leak.
Step 2: Inspect Common Leak Sites
✅ Toilets (Biggest Culprit!)
- Add food coloring to the tank. If color seeps into the bowl within 15 mins, replace the flapper.
✅ Faucets & Showerheads
- Look for drips or mineral buildup (a sign of slow leaks).
✅ Under Sinks & Appliances
- Feel pipes for moisture, check for warped cabinets (hidden leaks).
Step 3: Monitor Your Water Bill
- Compare monthly usage. A sudden spike with no behavior change = leak.
Low-Flow Showerheads vs. Faucet Aerators: Which Cuts Most Waste?
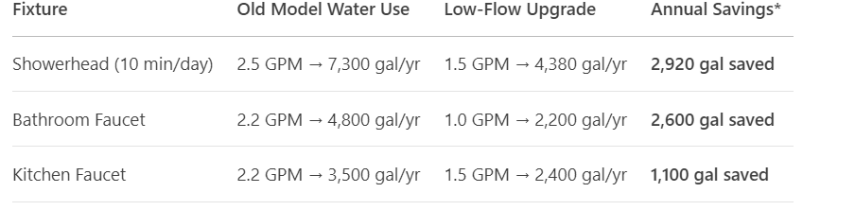
*Savings estimates for a 2-person household. GPM = Gallons Per Minute.
Best Upgrades:
- Showerhead: Niagara Earth Massage (1.5 GPM, $35, high pressure).
- Aerator: Neoperl 1.0 GPM (swivel design, $8).
Smart Water Leak Detectors: Top Picks
Prevent disasters with these Wi-Fi-connected guardians:
- Phyn Plus ($600)
- Pros: Installs on main water line, detects micro-leaks, shuts off water automatically.
- Best For: Whole-home protection (pricey but worth it).
- Moen Flo ($500)
- Pros: Alerts for pipe freezes, integrates with Alexa.
- Cons: Requires professional installation.
- Govee Wi-Fi Water Sensor ($50/2-pack)
- Pros: Affordable, places near appliances/under sinks.
- Cons: Doesn’t shut off water—alerts only.
Pro Tip: Pair sensors with a $20 water shutoff valve (like Dome) for automatic cuts during leaks.
Final Checklist
🔧 This Weekend:
- Test toilets with dye tablets ($5 on Amazon).
- Install at least one low-flow aerator.
💡 Next Level:
- Add a smart shutoff valve if you have frequent leaks or vacation often.
Next Up: Community Water Solutions—How to Advocate for Local Conservation.

Community & Policy Engagement: Amplify Your Water Impact
Individual action matters—but collective change creates unstoppable momentum. Here’s how to join forces with neighbors, push for policy upgrades, and launch viral water-saving campaigns that transform entire communities.
Cities Leading the Water Conservation Charge
These urban areas prove conservation works at scale:
💧 Tucson, AZ
- Rebates: $2,000 for rainwater harvesting systems, $500 for greywater installs.
- Result: 30% drop in per-capita water use since 1990.
💧 Melbourne, Australia
- Mandatory Targets: 155 liters/person/day during droughts (vs. 247 liters previously).
- Tool: Public “water map” shames/rewards neighborhoods.
💧 Las Vegas, NV
- Lawn Removal Pays: $3/sq ft to replace grass with desert landscaping.
- Saved: 9 billion gallons annually—enough for 72,000 homes!
Your Move: Google “[Your city] + water rebates”—most programs go unused!
How to Petition for Local Water Incentives
- Gather Data
- Calculate local water waste stats (ask utilities for leak reports).
- Find model policies from cities above.
- Build a Coalition
- Partner with community gardens, eco-businesses, and PTAs.
- Meet Decision-Makers
- Request 10 mins at a city council meeting with a 1-page proposal (template here).
Pro Tip: Pitch rebates as economic stimulators—every $1 invested in conservation saves $3-8 in new infrastructure costs (EPA).
Social Media Campaigns That Made Waves
📱 #DroughtShaming (Cape Town)
- Residents posted pics of water-wasting neighbors.
- Result: Cut daily use by 50% during “Day Zero” crisis.
📱 #SlowTheFlow (Utah)
- Viral videos of kids fixing leaks.
- Result: 5 million gallons saved in 3 months.
Your Turn: Start a “100-Gallon Challenge”—tag friends to share their best water hack.
One Action to Take Today
🔹 Comment on a local water agency’s Facebook post demanding expanded rebates.
Next: Final Water Wisdom—Your Legacy as an Urban Water Warrior.
Be the Change: Your Water-Wise Journey Starts Now
Every drop saved in your urban homestead adds up to rivers of change. Let’s recap your biggest opportunities:
💧 Quick Wins
- Fix leaks (a dripping faucet wastes 3,000+ gallons/year)
- Install a rain barrel (collect 600+ gallons annually from just 1″ of rain)
- Switch to drought-proof plants (like rosemary or okra)
🌱 Long-Term Impact
- Advocate for water rebates in your community
- Share your successes (#UrbanWaterHero) to inspire neighbors
Your Challenge Today:
Pick just one strategy from this guide to implement this week—whether it’s adding mulch to your garden or testing your toilet for leaks. Small steps create unstoppable momentum.
We’d love to hear your story!
👇 Comment below:
• What’s your #1 water-saving hack?
• Which tip will you try first?
Together, we’re building a future where every urban homestead thrives—one smart drop at a time.
Stay tuned for more sustainable living tips—subscribe below!



